In the mid-1990s, Dakota Gas saw opportunities in the fertilizer business and built an anhydrous ammonia plant on site. Anhydrous ammonia is used as fertilizer for farming and as a feedstock for producing various chemicals.
Dakota Gas' expertise acquired in manufacturing and marketing ammonia products since the 1990s is a valuable tool for Basin Electric's future.
Step-by-step anhydrous ammonia production
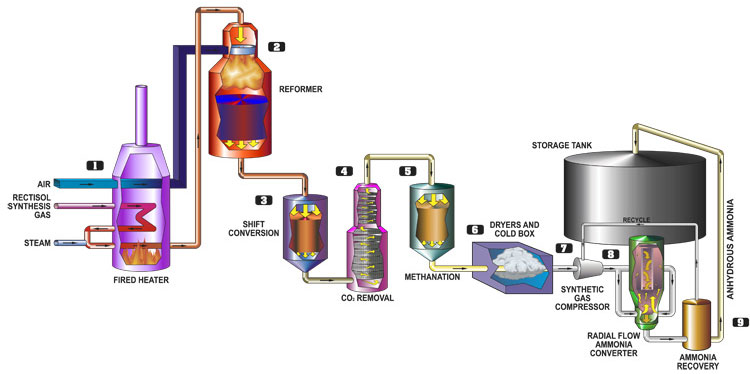
- Rectisol synthesis gas, air and steam are heated by a fired heater using synthetic natural gas as a fuel. These heated gases are introduced into
- the reformer where the methane is converted to carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The exit gases from the reformer enter
- shift conversion where the carbon monoxide and water react to form hydrogen and carbon dioxide. In the
- carbon dioxide removal vessel, an absorption process is used to remove the carbon dioxide. The stream from the carbon dioxide removal system still contains small amounts of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide so it is sent through
- the methanator where they react with hydrogen to form methane. Before the stream can be introduced to the ammonia synthesis loop, the
- dryers and cold box remove water and methane along with excess nitrogen so that the hydrogen and nitrogen ratio equals three to one.
- The synthetic gas compressor takes the fresh feed from the cold box plus the ammonia loop recycle stream and compresses it to 2500 psig. As the stream travels through
- the radial flow ammonia converter, the hydrogen and nitrogen react to form ammonia.
- The ammonia recovery unit then cools the stream and the liquid ammonia is sent to the 30,000 ton ammonia tank where it is stored until it is sold. The recycle gases are then returned to the synthetic gas compressor for reintroduction into the ammonia converter.

